Date:2025/07/07 12:26:24
Column:Validation and Verification on GHG Emission Reductions
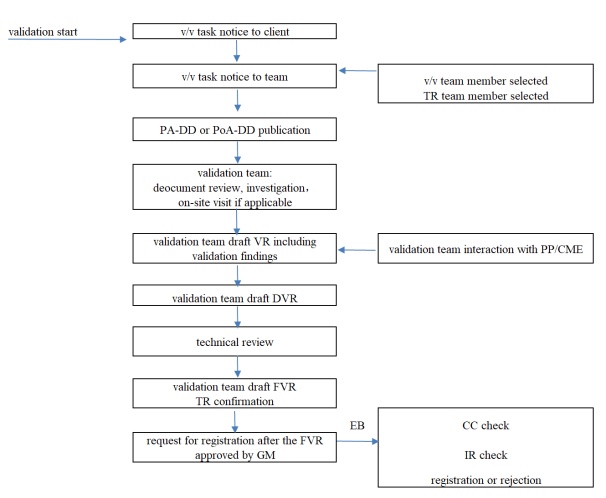
Validation / Verification / Certification ProcessFlow Chart
Validation
Validation is the process of independent evaluation of a CDM project activity or PoA by a DOE against the requirements of the CDM rules and requirements as set out in CDM modalities and procedures and relevant decisions of the Kyoto Protocol Parties and the CDM Executive Board (EB), on the basis of the PDD or PoA-DD and CPA-DDs.
A validation contract will be signed between CEC and the CDM project participant(s)/CME(s). CEC will start the formal validation process when related application documents (including the PDD) were received. the validation process includes: making PDD publicly available, desk review, on-site visit and assessment (if applicable), and completion of draft validation report, internal technical review, completion of final validation report and submission of request for registration to EB. CDM EB will make the report publicly available and register this project as an official CDM project if no other issues were identified.
The validation process flow presents as below:
Verification/ Certification
Verification is the periodic independent evaluation and ex post determination by a DOE of monitored GHG emission reductions or net anthropogenic GHG removals that have occurred as a result of the registered CDM project activity or PoA.
Certification is the written assurance by a DOE that, during a specified time period, the CDM project activity or PoA achieved the GHG emission reductions or net anthropogenic GHG removals, as verified.
A verification contract will first be signed between CEC and the CDM project participants/CME(s) for the verification/certification process. CEC will start the formal verification process after the related application documents received. The verification process includes: publication of the Monitoring report, desk review, on-site assessment, completion of draft verification/certification report, internal technical review, competition of final verification/certification report, submission of request for issuance to EB. Then EB will make the report publicly available and issue CERs (Certified Emission Reduction credits) if no other issues were identified.
The verification process flow presents as below:

Note:This information is publicized in both English and Chinese. In the event of any conflict or ambiguity or discrepancy between the two versions, the Chinese version shall prevail.